Every Thursday, the Tahoe Fund shares a Fun Fact about Tahoe straight to your inbox! Don’t miss it, sign up using the box on the left of this page.





























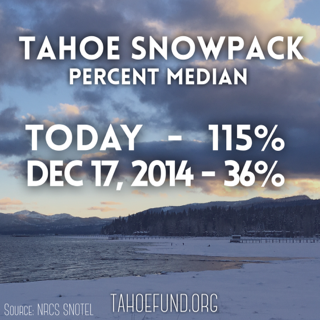




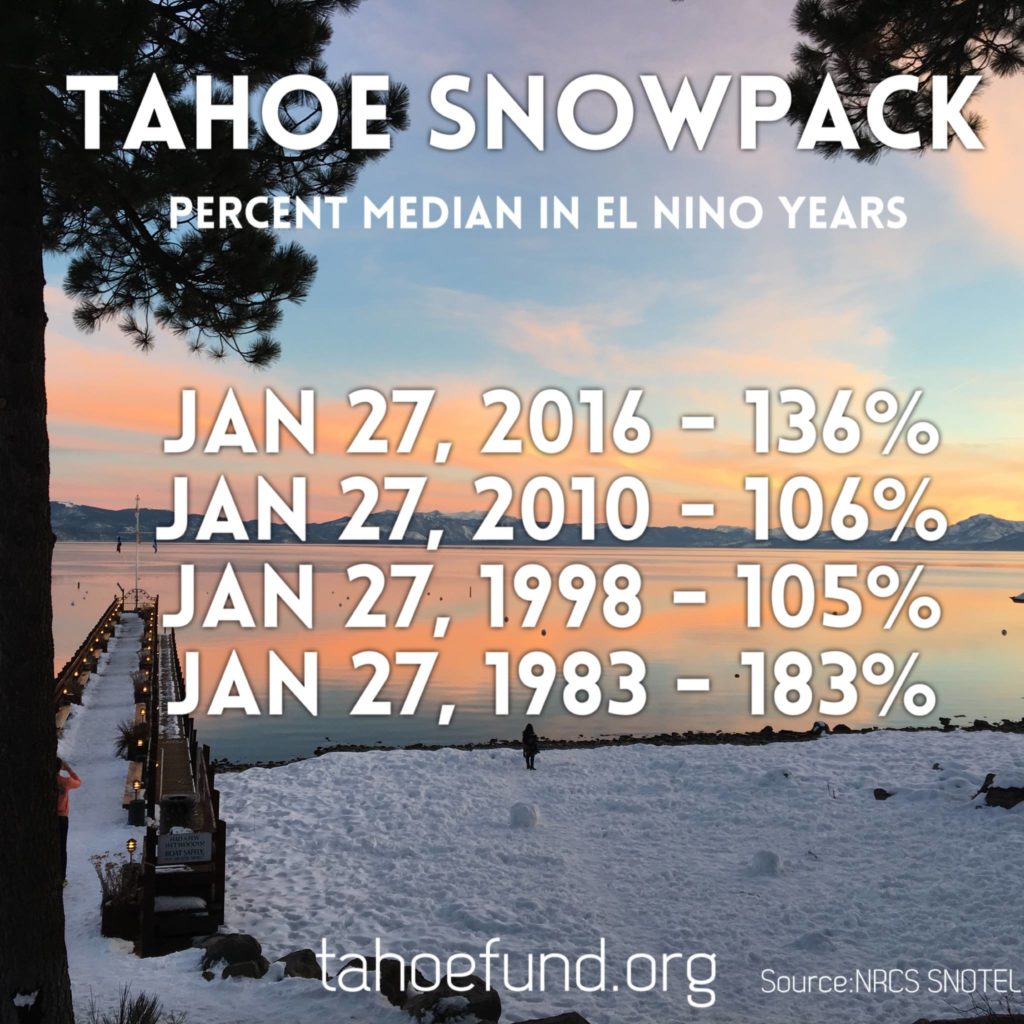




















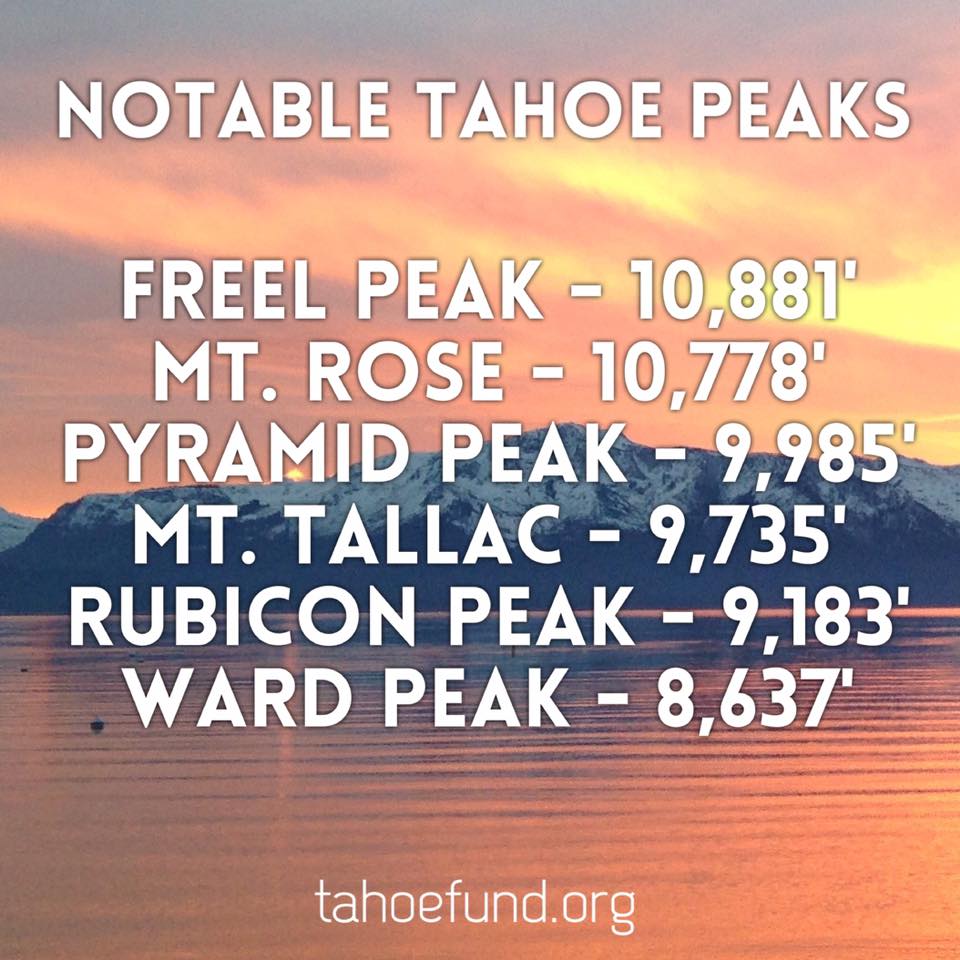











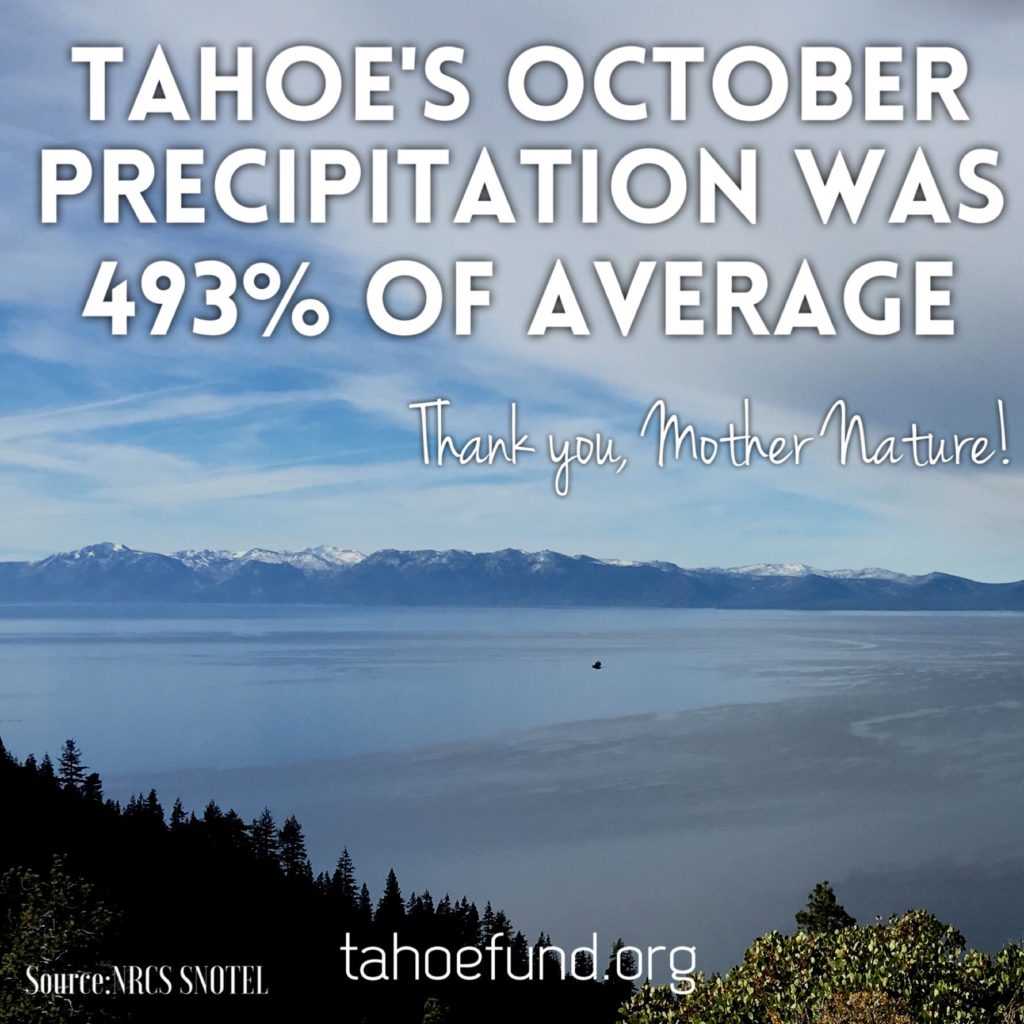


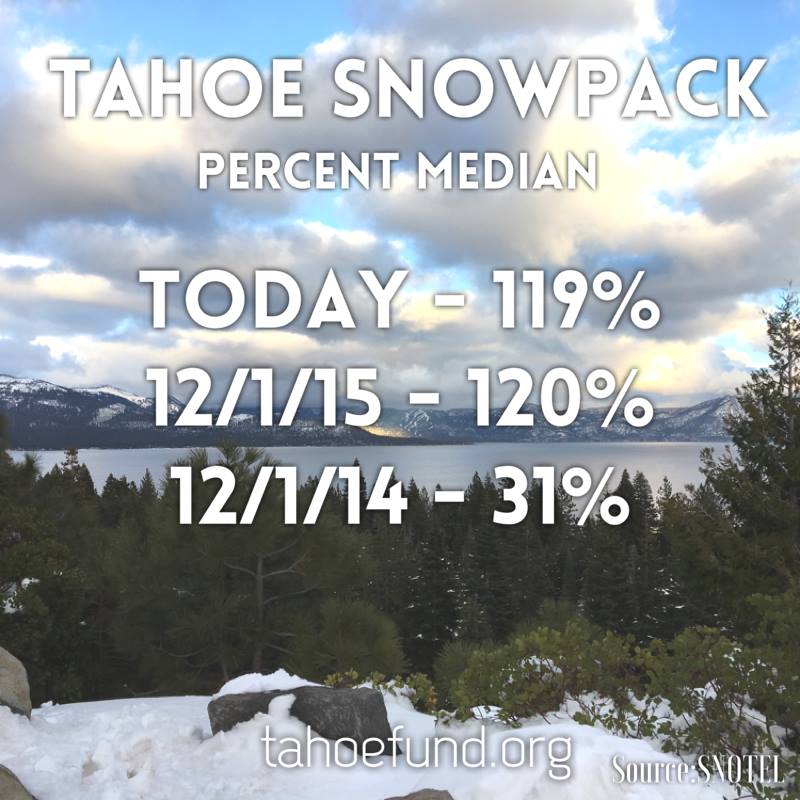












































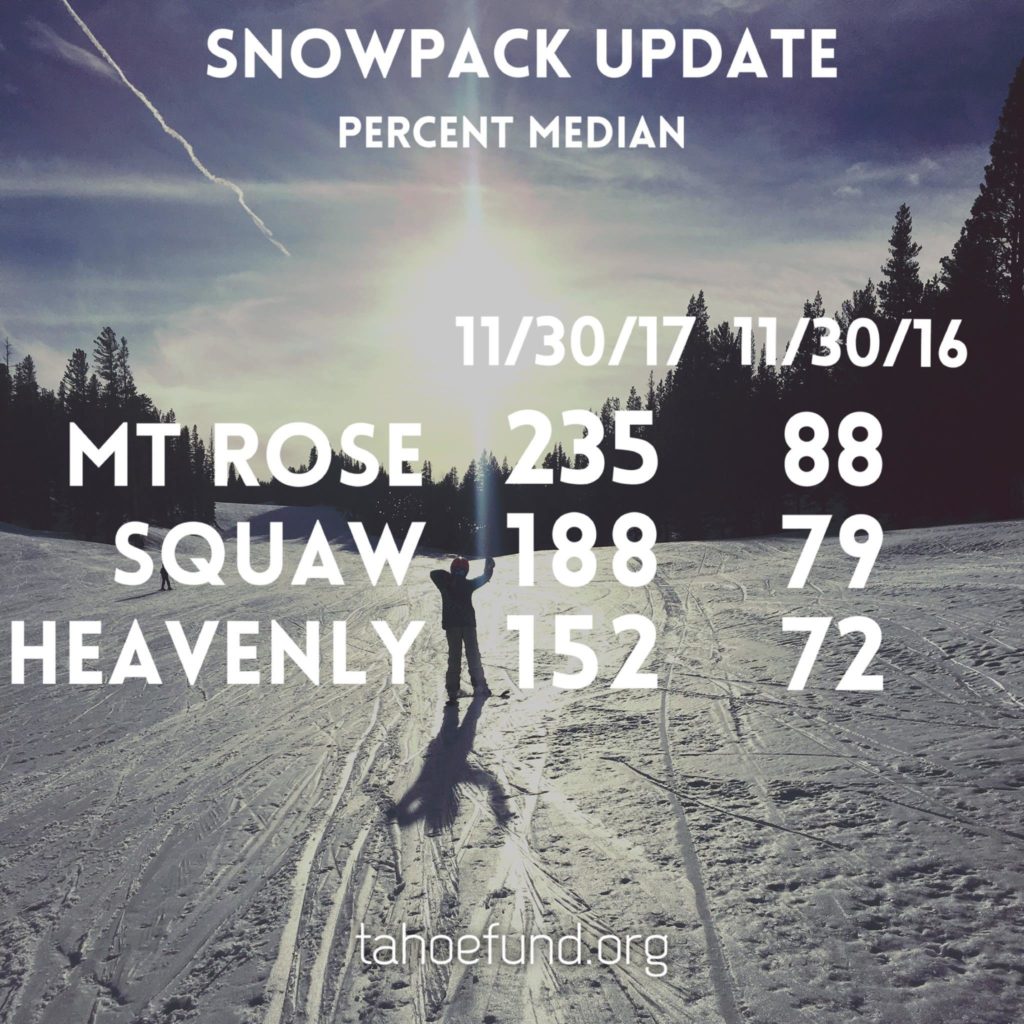

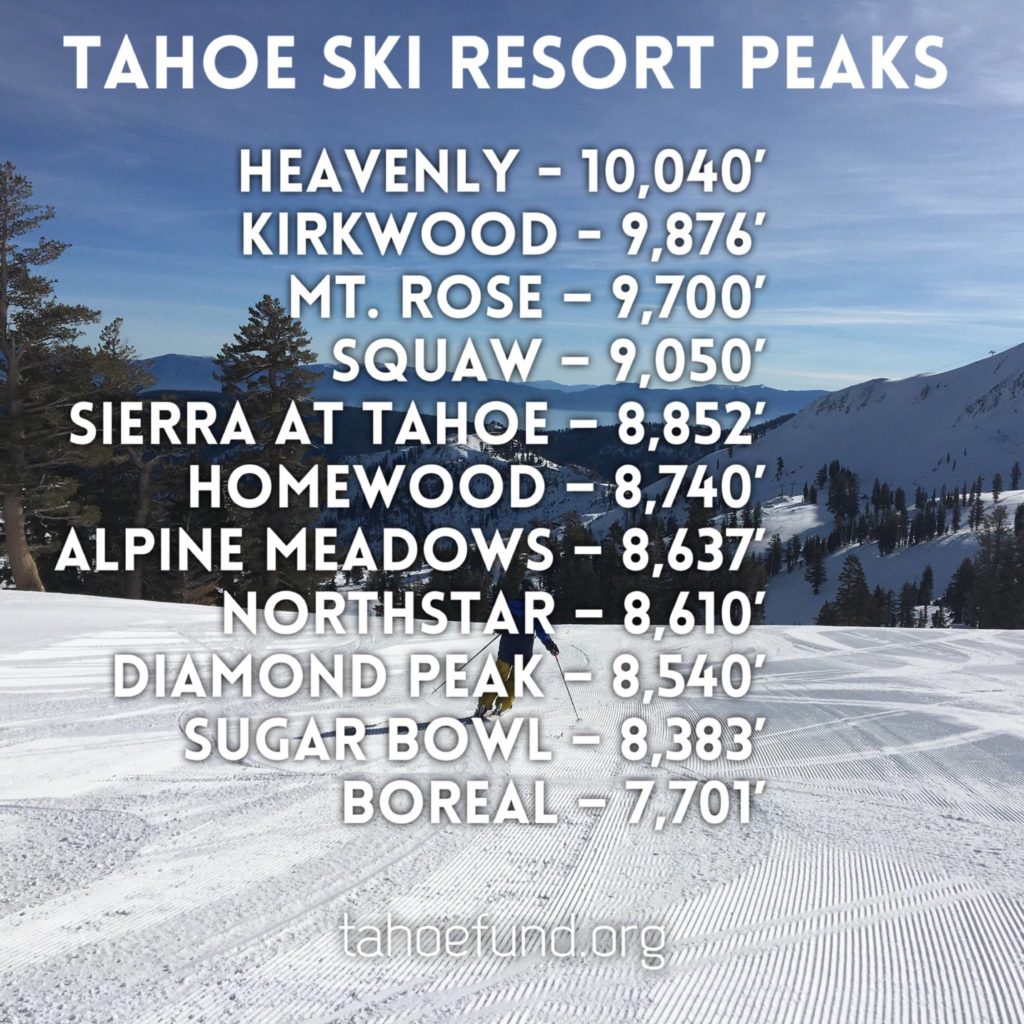
















































































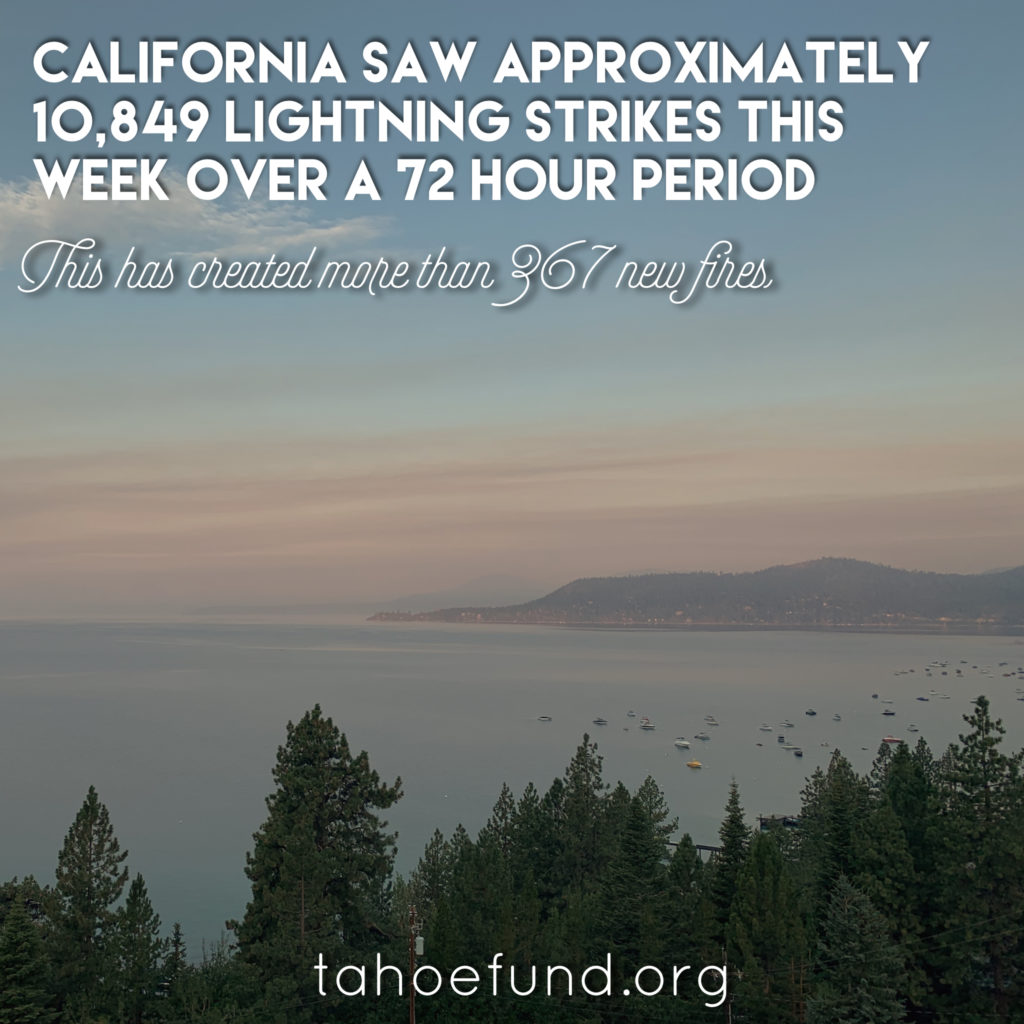







The only thing that runs deeper than Tahoe is our desire to preserve it all, so you can enjoy it all. Here are some Lake Tahoe Fun Facts to help you do just that.
Information below provided by tahoefacts.com, Courtesy of David C. Antonucci an environmental engineer and 34-year Tahoe resident. Tahoe FAQs were prepared in cooperation with the UC Davis, Tahoe Environmental Research Center.
How did Lake Tahoe form?
Three to five million years ago, the valley that would become the Tahoe Basin sank between parallel fractures in the Earth’s crust as the mountains on either side continued to rise. A shallow lake began to form in the resulting valley. Two to three million years ago, erupting volcanoes blocked the outlet on the north end, forcing the lake to raise hundreds of feet above its current elevation, and eventually eroding down to near its current outlet. Between one million and 20,000 years ago, large masses of glacial ice covered the west side of the Tahoe Basin. Current geologic theory suggests an earthen berm (moraine) on the Truckee River left by a receding glacier near Squaw Valley, or the glacier itself, acted as a dam. This caused the lake level to rise and then draw down rapidly when the dam catastrophically failed. The epic-sized flood washed boulders the size of cars past present-day Reno, Nev. Between 7-15 thousand years ago, a four-mile segment of the West Shore collapsed into the Lake. The cataclysmic event caused a massive submerged debris avalanche, produced a 300-foot high tsunami and widened the Lake by three miles.
How did the name Tahoe originate and what does it mean?
The name Tahoe comes from a mispronunciation of the Washoe Native American name for Lake Tahoe, da ow a ga, which means, “edge of the lake.”
Where is the Tahoe Basin located?
The Tahoe Basin straddles the California-Nevada border. The coordinates of the geographic center of the main body of Lake Tahoe are 39° 06’ 30” N and 120° 01’ 51” W. Lake Tahoe and its watershed span the montane and subalpine life zones.
How high is the Tahoe Basin?
The surface of the Lake is at an elevation of 6,225 feet above historical sea level. The surrounding mountain peaks vary from 9,000 to nearly 11,000 feet. Only 16 other large lakes in the world are higher.
How pure is the Lake?
The water is 99.994% pure, making it one of the purest large lakes in the world. For comparison, commercially distilled water is 99.998% pure. Tahoe contains roughly 60 parts per million of dissolved matter.
Why does the Lake appear to have different colors?
As light penetrates the Lake, water molecules absorb various colors. Fine particles and the exceptional clarity allow backscattering of the predominating light color toward the eye of an observer. The lake water appears blue as other colors in the light spectrum are absorbed at deeper depths and the predominant blue light is scattered back toward the observer’s eye. The center of the Lake can appear cobalt blue, as blue light is absorbed further, leaving visible violet light as the predominant light color. In shallow areas, the water can appear emerald or turquoise in color since green is the predominant light color at shallow depths. In addition, under the right conditions, the Lake surface can reflect the adjacent mountains and the color of the sky.
How clear is the water and why?
Clarity is determined by measuring the water depth at which an 8-inch diameter white disk disappears from view. The Lake owes it extraordinary natural clarity mainly to its exceptional depth and volume, a relatively small watershed and favorable climatological conditions. In 2008, clarity averaged 69.6 feet, far less than the maximum 105 feet of clarity measured in 1968. In the last eight years, the rate of loss of clarity has decreased due to environmental improvements in the watershed.
How large is the Lake?
The maximum length of the Lake is 21.2 miles (north to south) and the maximum width is 11.9 miles (east to west). The surface area is 191 square miles (122,200 acres). The shoreline length is 75.1 miles and the encircling state highway is 71.8 miles long.
How deep is the Lake?
A maximum depth of 1,645 feet in Crystal Bay makes Tahoe the second deepest lake in the USA, third deepest in North America and 11th deepest in the world. The elevation of Carson City, Nevada is 85 feet higher than the deepest part of Lake Tahoe. If the Willis (formerly Sears) Tower, the tallest building in North America, were dropped into Lake Tahoe at its deepest point, the top would still be submerged by 195 feet of water. The average depth is about 1,000 feet.
How much water is in the Lake?
The Lake holds about 39 trillion gallons of water, enough to cover the state of California to a depth of 14½ inches. A dam at Tahoe City on the Lake’s outlet regulates the upper 6.1 feet of Lake Tahoe above the low water mark. Between the regulated high and low water levels, the volume of water in Tahoe can vary by 243 billion gallons. Tahoe is the sixth largest lake in the USA.
How old is Lake Tahoe?
Lake Tahoe is over 2 million years old. Tahoe is considered an ancient lake and is counted among the 20 oldest lakes in the world.
How does Lake Tahoe compare to other world lakes?
Tahoe is the second largest lake in the world at or above this elevation. It is the 31st largest lake overall and the 11th deepest lake in the world.
Where does the water come from?
Rain and snow melt runoff from 63 tributaries in the 312 square-mile watershed adds 65% of the water. Another 35% falls as precipitation directly on the Lake. Typically, 212 billion gallons of water enter the Lake this way each year. In a normal year, Lake Tahoe will rise 15 inches from spring runoff, assuming the outlet gates are closed.
Where does all the water go?
About one-third of the water flows into the Truckee River through the dam at Tahoe City for downstream use with any remaining water flowing 140 miles to the river terminus at Pyramid Lake. The remaining two-thirds of water evaporate from the lake surface at an annual average rate of 0.1 inch per day. The average daily evaporation of water from the lake surface would serve the daily needs of 3.3 million Americans.
What is the weather like?
During the winter months, the average high air temperature is in the mid-40s °F and the average low is in the mid to high-20s °F. In the summer months, the average highs are in the low-80s °F and the lows in the mid to low-50s °F. At least seven months per year, daily maximum temperatures reach the outdoor comfort zone. Sunshine occurs over 75% of the time during daylight hours each year for 273 sunny or partly sunny days. From November through March, 78% of the yearly precipitation occurs, mostly as snowfall. Typically, at lake level in Tahoe City, 15.8 feet of snow falls over winter and accumulates to a maximum snow pack depth of 2.8 feet Summers are very dry and there is less than a 10% chance of getting more than 0.1 inch of precipitation between May 1 and October 15.
How cold is the Lake?
Below an average depth of 900 ft, water temperature is a near constant 40˚F. Over the last 10 years, monthly surface water temperature averaged 41.9˚F at its coldest in February and 65.7˚F at its warmest in August. Daily maximum surface temperature can reach 75˚F. Over the past 38 years, water temperature warmed an average of 1˚F from top to bottom and monthly water surface temperature increased 1.6˚F due to global climate change.
Does the Lake ever freeze?
The main body of Lake Tahoe does not freeze. The stored heat in the Lake’s massive amount of water compared to its relative surface area prevents the Lake from reaching freezing temperature under the prevailing climatic conditions. On rare occasions, Emerald Bay has developed full or partial ice cover and thin ice sheets can form on shallow near shore waters under very cold and calm conditions.
Does pollution endanger Lake Tahoe?
Tahoe has lost about one-third of its world-renowned clarity since 1968. The major component of clarity loss is fine particles, with nearly three-quarters originating from development-impacted watersheds. Another important pollutant is nitrogen, over one-half of which comes from atmospheric fallout created by vehicle exhaust and pollution blown in from surrounding urban areas. A third critical pollutant is phosphorus, with disturbed and natural watersheds contributing two-thirds of the load. All wastewater is treated and exported from the Basin. Lake Tahoe is designated an Outstanding National Resource Water under the Federal Clean Water Act.
How many people are at Lake Tahoe?
Year-round resident population is 40,000. Total population can reach 300,000 on peak days. About 15 million people visit Lake Tahoe each year.